The active car safety sensors improve the quality of decisions made by drivers. They’re a new technology system that constantly monitors a motor vehicle and the environment around it.
Furthermore, they act as driver aids by displaying this information to the driver on the dashboard display screen. The intelligent parking assist systems are part of the car safety features.
They offer collision warning and assist in vehicle control. Safety sensors issue both image and audio alerts. For example, seat belt sensors which beep when you’re not buckled up.
What is the purpose of safety sensors in cars?
Safety sensors are different from active sensors. Generally, this car safety feature monitors and identifies potential hazards.
However, their functionality varies depending on their specific function and application. Furthermore, safety sensors activate a response to mitigate or prevent harm.
What is the difference between an active safety sensor and a safety sensor?
A safety sensor refers to any type of sensor used in a vehicle to assist drivers and to provide information to various vehicle systems. For example, airbag deployment sensors, tire pressure monitoring sensors, stability control sensors amongst others.
Safety sensors are not directly involved in preventing accidents or aiding the driver in real-time. However, active safety sensor performs real-time monitoring of the vehicle’s surroundings and takes actions to prevent accidents or active driver assistance.
For example automatic emergency braking, parking assistance systems blind spot monitoring. Active safety sensors gather data about the road, traffic, and nearby objects.
They’re known for theses features; collision avoidance, lane departure warnings, automatic emergency braking, adaptive cruise control, and more.
Understanding active safety sensors in cars
Active safety sensors actively intervene to prevent accidents. Some of their features include, automatic emergency braking and lane departure warning systems.
They constantly monitor the environment around the vehicle and alert drivers via images and audios. Therefore, this enhances road safety by significantly reducing the risk of collisions.
Sensor based car safety features detect potential hazards and provide timely warnings. Additionally, they help drivers to avoid accidents and make safer driving decisions. For example, automatic steering.
Automatic emergency braking.
Automatic emergency braking is one such feature that utilizes active safety sensors. It detects when a collision with another vehicle or obstacle is imminent.
Accidents or collisions could occur because the driver has lost control of the steering or he/she hasn’t assessed the car blind spot. Afterwards the car safety features automatically applies the brakes to prevent or mitigate the impact.
Lane departure warning systems
Lane departure warning systems are another important application of active safety sensors. They monitor the car’s position within its lane and issue alerts if it detects unintentional drifting or veering off course.
This helps drivers stay in control of their positioning on the road, preventing them from inadvertently crossing into adjacent lanes or off-road areas.
By constantly scanning the surroundings, these sensors act as an extra set of eyes for drivers. They assist in vehicle control and safe navigation through various traffic conditions.
Lastly active safety sensors provide real-time information about potential risks on the road.
Types of connected car sensors for road safety
Connected car sensors offer real-time communication between vehicles and infrastructure like traffic lights, centralized systems and road signs.
They form part of the backbone of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). Additionally, they provide accurate data about traffic conditions, and more.
The following are some of the technologies that make it possible for their full functionality.
Global Positioning System (GPS).
GPS sensors help cars determine their precise location on the road, ensuring accurate navigation and route guidance. Additionally, GPS systems also allow drivers to get area specific alerts.
They also facilitate setting up of a geofence. Such that the vehicle’s owner receives alerts on their devices when the vehicle crosses a set digital boundary.
Radar.
Utilizing radio waves, radar sensors detect objects around the vehicle, including other cars, pedestrians, or obstacles. They’re great collision avoidance systems and form part of the components of adaptive cruise control systems.
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR).
LiDAR sensors use laser beams to create detailed 3D maps of the surroundings. By measuring distances and identifying objects with precision, LiDAR enhances autonomous driving capabilities.
Cameras.
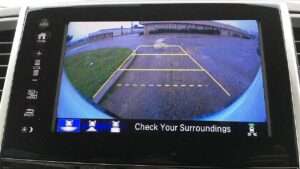
They’re equipped with image recognition technology for capturing visual data such as lane markers and road signs. Secondly, cameras monitor the car’s surroundings to spot obstacles, other vehicles and pedestrians which also works for parking assistance systems.
They send the image data to other safety systems. This visual input assists in lane departure warning systems and traffic sign recognition.
Drivers share the information gathered through connected car sensors that are enabled with wireless communication. Afterwards the drivers can make informed decisions on the road while also contributing to overall road safety.
Whether it’s detecting nearby vehicles using radar or analyzing lane markers through cameras, these sensors enhance situational awareness for both drivers and autonomous vehicles alike.
Innovations in sensor technology for improved car safety.
Advancements in sensor technology have transformed car safety measures. Newer sensor technologies offer higher accuracy and faster response times.
Therefore, this enhances the overall safety of automobiles. These innovations have paved the way for improved hazard detection and prevention.
Integration of artificial intelligence (AI).
By leveraging AI capabilities, car sensors can now analyze and interpret data more effectively. Hence enabling them to detect potential hazards with greater precision.
Secondly, artificial intelligence highly contributes to the optimum performance of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). This has made autonomous cars safer on the roads.
Radar-based sensors.
Radar-based sensors are a product of the continuous research and development efforts by manufacturers. Their efforts intention is to drive further improvements in sensor technology.
They are constantly exploring new ways to enhance safety technologies through sensor advancements. The radar-based sensors enable adaptive cruise control systems to maintain a safe distance from other vehicles automatically.
Camera-based sensors.

Camera-based sensors are another innovation that has revolutionized car safety. They provide visual information to assist in various safety features such as lane departure warning systems and pedestrian detection.
Furthermore, their use in intelligent parking assistance systems reduces the stress involved in parking maneuvers. These camera-based sensors work together with other car safety devices like radars to create a comprehensive safety network within the vehicle.
Different types of car safety sensors and their functions.
Proximity Sensors:
Proximity sensors are an essential component of modern cars, helping drivers with parking and collision avoidance systems. By detecting objects near the vehicle, these sensors provide timely alerts to prevent accidents.
Speed Sensors:
This type of car sensors play a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance of anti-lock braking systems (ABS). They’re responsible for translating the rotation rate of different vehicle components into a speed value.
Wheel speed sensors measure the rotation speed of the wheels, allowing the ABS to adjust braking pressure accordingly. Further preventing wheel lock-up during emergency braking.
Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS):
The TPMS utilizes pressure sensors to monitor tire pressure levels in real-time. This system alerts drivers when tire pressure drops below safe thresholds.
Low tire pressure impacts handling, fuel consumption or potentially lead to a blowout. TPMS enhances safety on the road by keeping drivers informed about tire conditions.
Collision Detection Sensors:
Equipped with collision detection sensors, cars can identify potential crash risks by monitoring distances from other vehicles or obstacles. These sensors use advanced technologies such as radar or cameras to assess the surroundings accurately.
In critical situations, they provide warnings or assist with autonomous emergency braking systems. Collision detection sensors also form part of the parking assistance systems.
In addition to these commonly known car sensors for safety purposes, there is another important sensor worth mentioning.
The oxygen sensor.
Although not directly related to safety functions, oxygen sensors monitor exhaust gases and help optimize fuel efficiency while reducing emissions. They ensure that the engine operates at its best performance while minimizing environmental impact.
Other sensors like the mass airflow sensor in modern vehicles enhance safety measures and enable operational performance. These technologies work together seamlessly.
Safeguarding automotive sensors for optimal safety performance.
Maintenance and cleaning.
Regular maintenance and cleaning of automotive sensors ensure accurate readings. By keeping these sensors free from debris, dust, and other contaminants, their performance can be optimized for enhanced safety on the road.
Protection.
Protecting sensors from physical damage is crucial for their proper functioning. Their placement is on the car’s body in vulnerable areas such as bumpers or side mirrors.
Therefore, this makes the sensors susceptible to impacts that may impair their accuracy. Employing protective measures like bumper guards or sensor covers can safeguard these critical components.
Calibration of sensors.
Calibration of sensors is necessary to maintain their accuracy over time. Slight deviations in readings may occur as automotive sensors age, .
Regular calibration ensures that these deviations are corrected, allowing the sensors to provide precise data for optimal safety performance.
Sensor wiring.
Ensuring the integrity of sensor wiring and connections enhances safety performance. Loose or damaged wiring can lead to inaccurate readings or complete sensor failure. Regular inspections should be conducted to identify any issues with wiring or connections and address them promptly.
By adhering to these practices, automotive sensors can function at their best, providing reliable data for a safer driving experience.
Exploring the role of sensors in preventing accidents and collisions
Sensors play a crucial role in enhancing safety on the roads by providing early warning signals to drivers. These technological marvels enable prompt reactions, helping prevent potential collisions and accidents.
Collision detection sensors.
These active car safety sensors are equipped with collision warning capabilities for monitoring the proximity of objects and barriers around the vehicle.
In case of an imminent collision, they alert the driver through visual or auditory cues, allowing for immediate action. This feature proves invaluable in avoiding forward collisions.
Automatic crash notification.
In unfortunate instances where a collision does occur, sensors are designed to automatically notify emergency responders about the accident.
Such sensors in car safety features have a connection to the wireless communication network. Furthermore, they are programed with emergency contacts.
This real-time information enables quicker response times and enhances the chances of timely assistance.
Lane departure warning systems.
By utilizing sensors, vehicles can now detect when drivers unintentionally drift out of their lane. The system promptly alerts them through audible warnings or vibrations, preventing potential accidents due to distracted driving or drowsiness.
Adaptive cruise control systems.
Sensors integrated into adaptive cruise control systems continuously monitor the distance between vehicles on the road. Additionally, these systems use data from sensors to navigate through traffic after taking over the car’s control.
They adjust the speed accordingly to maintain a safe following distance, reducing the risk of rear-end collisions. Further, they actively assist drivers to drive by issuing inputs and the driver doesn’t have to drive the car.
Addressing Common Concerns about Car Safety Sensors
Privacy Concerns
Data collection by car safety sensors may raise privacy concerns. Strict regulations are in place to protect personal information. Personal data collected by car safety sensors is safeguarded.
Sensor Reliability
Continuous testing and improvement ensure sensor reliability. Rigorous quality control measures are implemented. Sensors undergo regular maintenance and calibration.
False Alarms
False alarms triggered by car safety sensors are rare but can occur. Certain situations, such as extreme weather conditions or temporary obstructions, may lead to false alarms.
Manufacturers work to minimize false alarms through advanced algorithms and detection mechanisms.
Redundancy Features
Car safety sensors are designed with redundancy features. Redundancy ensures that failures in individual sensors do not compromise overall vehicle safety. Reverse or backup systems and multiple sensor installations provide additional layers of protection.
Importance of active safety sensors in enhancing Car Safety
Active safety sensors play a crucial role in enhancing car safety by actively intervening in critical situations and reducing the risk of accidents.
These sensors are designed to detect potential hazards and take immediate action to prevent collisions or minimize their impact.
Automatic emergency braking systems.
One essential application of active safety sensors is in automatic emergency braking systems. These systems utilize active safety sensors to continuously monitor the surroundings and detect potential collisions.
When a potential collision is detected, the system applies the brakes automatically, helping to prevent accidents or reduce their severity.
Lane keeping assist systems.
Active safety sensors are also used in lane keeping assist systems. These systems rely on sensors to monitor the vehicle’s position within its lane.
If the vehicle starts drifting out of its lane without signaling, the system provides corrective steering inputs to keep it safely within the lane.
Pedestrian detection systems.
Another important use of active safety sensors is in pedestrian detection systems. Vehicles can identify pedestrians near them by using these sensors.
Afterwards, the systems take appropriate action to avoid accidents. This technology has proven effective in preventing collisions with pedestrians, particularly in urban areas with high foot traffic.
A comprehensive guide to car safety features
Car safety features play a crucial role in ensuring the well-being of drivers and passengers. They are inclusive of airbags, seat belts, anti-lock braking systems (ABS), electronic stability control (ESC), and sensor-based technologies.
Sensor-based technologies.
They work with other safety features to provide comprehensive protection. Firstly, there are sensor based car safety features which monitor the vehicle’s operations.
They ensure normal operation standards within the vehicle’s set-up. Secondly there are those that monitor the car’s position and its surrounding environment.
These ones offer various real time features that assist the driver. For example, collision warning after detection systems, blind-spot monitoring, adaptive headlights, reverse camera and more.
Understanding different car safety features is essential when purchasing a vehicle. By being aware of the available options, you can make informed decisions that prioritize your safety on the road. Some notable examples of sensor-based safety features include:
What are some common types of car sensors?
Car sensors come in various forms depending on their specific function. There are safety sensors that ensure normal vehicle performance and active safety sensors that offer real time driver assistance.
Some common types of active safety sensors include proximity sensors (used for parking assistance), radar sensors (detecting objects at a distance), camera-based sensors (for lane departure warnings), and ultrasonic sensors (used in blind spot detection).
Can car sensors be disabled or turned off?
In most cases, car sensors cannot be manually disabled or turned off as they are integral to the safety systems of the vehicle. However, some vehicles may have options to adjust sensitivity levels or temporarily disable certain features.

